3D semantic segmentation
Adapt "KP-conv" to industrial facility point clouds.
References: KP-Conv, H. Thomas, et al., 2020.
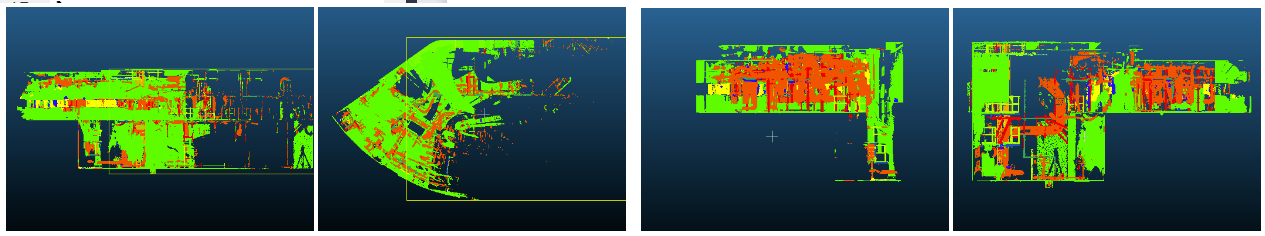
Summary: This project is part of a competition managed by the Data team (ENS Paris), in partnership with the Collège de France. The challenge is organised by EDF R&D. The goal to perform a semantic segmentation of a 3D point cloud. The point cloud of one EDF industrial facility digital mock-ups is composed of 45 billions of 3D points. The reconstruction work consisting of the fitting of 90 000 geometric primitives on the point cloud. To perform this task, the operators have to manually segment part of the point cloud corresponding to an equipment to then fit the suitable geometric primitive. This manual segmentation is the more tedious of the global production scheme. Therefore, EDF R&D studies solutions to perform it automatically.
Dataset: The boiling room was digitized with LiDAR scanners on tripods and contains 67 scanner positions. Each acquisition at one scanner position (which is called “station”) produces one point cloud of about 30 millions of points. The point clouds of the set of stations are registered in a single reference frame. Randomly subsampled point clouds will be provided. The train set contains 50 stations point cloud and the test set contains the remaining 18 stations.
Results: To solve this challenge, I used KP-Conv, a deep neural network build to classify and segment 3D point clouds. I ranked first in the competition with a score of 0.9400 on the private leaderboard. Details on the training and on the implementation can be found in the following pdf .
Ressources: I trained the network on Google Colab pro using a P100 GPU for 10 hours.