NAF
Zero-Shot Feature Upsampling
NAF
Loick Chambon Paul Couairon Eloi Zablocki Alexandre Boulch Nicolas Thome Matthieu Cord
arXiv 2025
Abstract
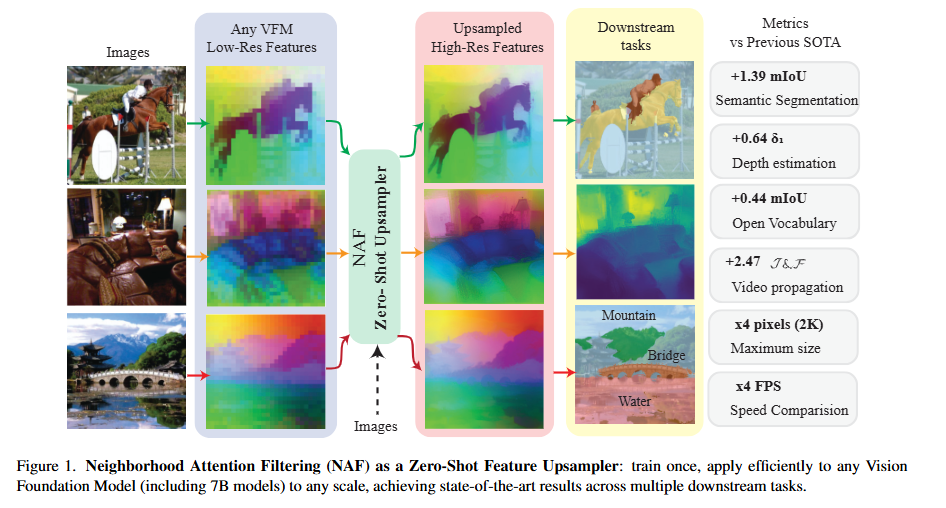
Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) produce downsampled spatial features, which are challenging for pixel-level tasks. Existing upsampling methods either rely on fixed classical filters (bilinear, bicubic, joint bilateral) or require learnable, VFM-specific retraining (FeatUp, LiFT, JAFAR). We introduce NAF — Neighborhood Attention Filtering — a zero-shot, VFM-agnostic upsampler that leverages Cross-Scale Neighborhood Attention and Rotary Position Embeddings (RoPE) to learn adaptive spatial-and-content weights guided solely by the high-resolution input image. NAF scales up to 2K feature maps efficiently (~18 FPS) and consistently outperforms previous methods across multiple downstream tasks, including semantic segmentation, depth estimation, zero-shot open vocabulary, and video propagation. It also demonstrates strong performance for image restoration.

Results
NAF allows efficient zero-shot upsampling of any VFM features to high-resolution. It achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple downstream tasks while remaining computationally efficient.
BibTeX
@misc{chambon2025nafzeroshotfeatureupsampling,
title={NAF: Zero-Shot Feature Upsampling via Neighborhood Attention Filtering},
author={Loick Chambon and Paul Couairon and Eloi Zablocki and Alexandre Boulch and Nicolas Thome and Matthieu Cord},
year={2025},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18452},
}